Introduction
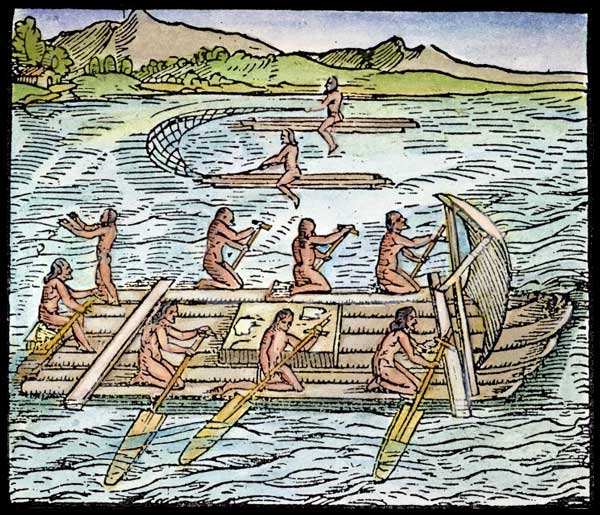
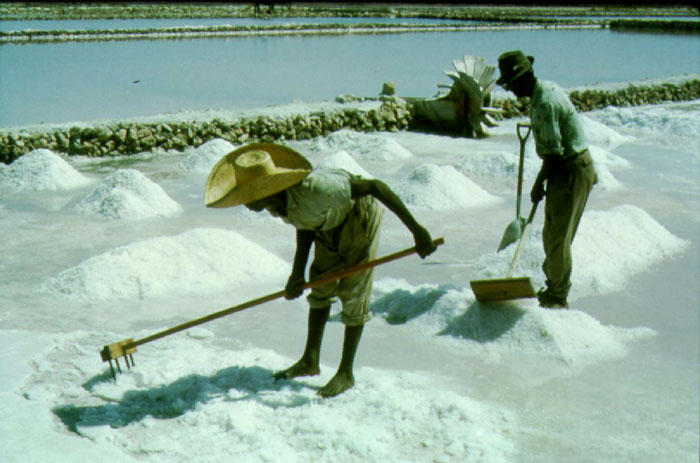
Slavery has played an important role in the development of the Islands. The first recorded African slaves were brought here by the Bermudans to work in the salt ponds.
Regulations in 1767 included slaves not being permitted to work on their own in any of the ponds, slave owners making good any damage caused by their slaves with the slaves receiving suitable punishment and any person buying or receiving salt from a slave without the permission of their master had to pay the master ten fold. Owners were also “accountable for the actions of their slaves, in case they damage any of the Inhabitants or Settlers at Turks Islands”. The “Royal Regulations”, accepted in 1781, included that no slaves were allowed to work for himself in any other ponds than those of his owner and that no person was allowed a share for any slave after the latter had been absent for more than forty-eight hours from the islands, an attempt to encourage slave owners to stop slaves running away. The masters also had to provide slaves when requested for public work.
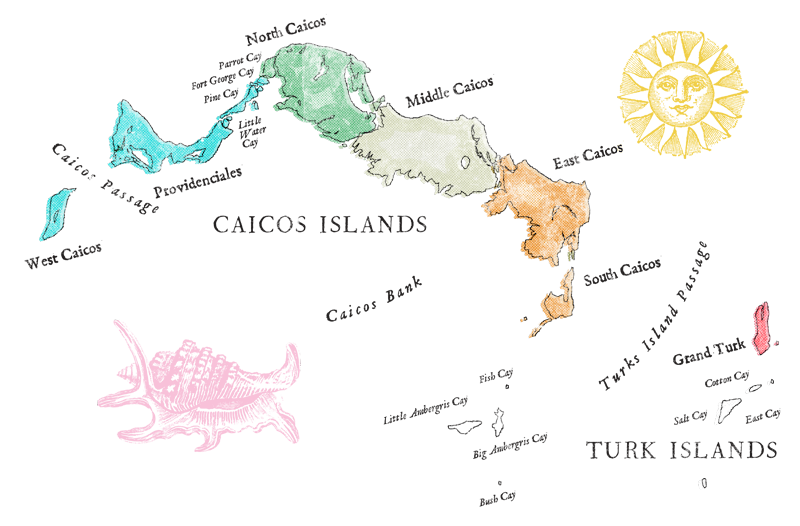
The next large introduction of slaves came when American Loyalist fled the USA after the War of Independence, setting up plantations on the Caicos Islands. In 1788 the Caicos Islands had a population of over 40 white families and 1200 slaves.
The Haitian revolution, begun in 1791, set up a free state for former slaves. This led to many slaves fleeing to Haiti: In 1800 the largest single slave escape in the Bahamas archipelago occurred when 14 of Wade Stubbs’ slaves stole a sloop: In 1821 many slaves fled from Grand Turk in salt lighters to freedom: In 1823 John Lightbourne’s slaves escaped from their barracks at Hawkes Nest and sailed to Haiti. A further exodus occurred in the schooner Polly, stolen from Henshall Stubbs at South Caicos.
Slaves received emancipation on 1st August 1834, the British Government paying slave owners ₤12 14s 4d for each slave. In theory the former slaves could now work for shares in the ponds or for wages.
In 1845 the leasehold system was introduced for the salt ponds, with all ponds entering the leasehold system in 1848. Those with money kept control of the ponds whilst removing traditional rights for the former slaves. Eventually, the former slaves were no better off, still working for their former owners but kept on the Island as they had to work to pay off debts raised during periods of unemployment. Many former slaves decided they wanted real freedom and wandered the islands possessing land and eking out a living from the land.
Emancipation doesn’t end the slave story. The Caicos Islands owe some of its population development to shipwrecked slaves. With slavery being illegal in British territories the slaves were freed, remaining in the Turks and Caicos Islands. In July 1837 a large slave ship wrecked near North Caicos. In 1841 Trouvadore sank off East Caicos while transporting 178 captives from Africa to the markets in Cuba. The rescued Africans were required to work for a year in Grand Turk and it was probably these freed slaves who established Bambarra on Middle Caicos in 1842.
Today, evidence remains of slavery in the plantation ruins and many locals bearing the surnames of plantation and salt pond owners. (N.B. The foregoing narrative is based on a paper presented by Nigel Sadler at the Museums Association of the Caribbean’s Annual General Meeting, October 2001. )
For more information
On this website see also The Salt Industry, and Slave Ship Trouvadore background. See also the Search for Trouvadore project website.